Physical Address
Introduction of Mumbai Trans Harbour Link

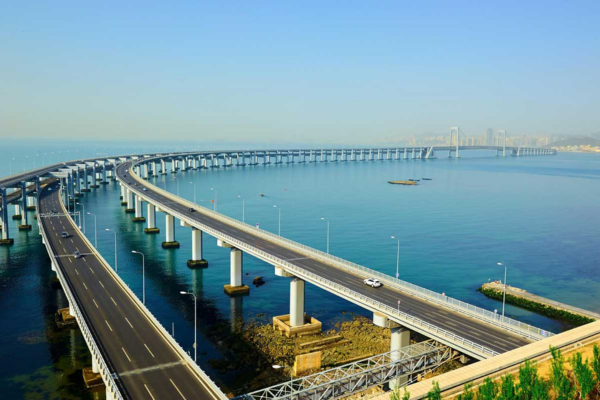
The Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL), also known as Atal Setu, stands as a monumental infrastructure project set to revolutionize connectivity in Mumbai. This ambitious project aims to bridge the gap between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, significantly reducing the travel time between these two bustling areas. Spanning approximately 22 kilometers, the MTHL will be the longest sea bridge in India, showcasing cutting-edge engineering and architectural prowess.
The need for the MTHL has been long-felt, given Mumbai’s chronic traffic congestion and the increasing demands of its expanding population. By providing a direct route across the Mumbai Harbour, this bridge is expected to ease traffic, boost economic activities, and enhance the overall quality of life for daily commuters.
But the MTHL is not just about easing traffic; it’s a symbol of progress and innovation. The project incorporates advanced construction techniques, sustainable practices, and smart technologies to ensure durability and efficiency. As the MTHL nears completion, it promises to be a transformative force, catalyzing growth and development in one of India’s most dynamic urban regions. Let’s explore the intricate details and construction marvels that make the MTHL a standout project in modern engineering.
Key Insights about Mumbai Trans Harbour Link: https://www.india-briefing.com/news/mumbai-trans-harbour-link-inaugurated-indias-longest-sea-bridge-key-insights-30746.html/
Historical Background of Mumbai Trans Harbour Link

Early Proposals and Planning
The concept of a trans-harbour link connecting Mumbai to Navi Mumbai has been contemplated since the 1970s. Early proposals envisioned a bridge that would seamlessly integrate the two regions, easing traffic congestion and fostering economic growth. However, these initial plans faced numerous challenges. The idea was ambitious for its time, requiring significant financial investment and advanced engineering capabilities that were not readily available. Detailed planning involved extensive feasibility studies, environmental impact assessments, and intricate designs to address the unique geographical and urban landscape of Mumbai. Despite the enthusiasm, these early proposals often stalled due to lack of funding, bureaucratic inertia, and the complexity of coordinating among multiple government agencies and stakeholders. The vision, however, persisted, driven by the undeniable need for improved connectivity and urban development.
Initial Challenges and Delays
The journey from concept to construction of the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link has been fraught with challenges and delays. Financial constraints were a major hurdle, with funding initially hard to secure for such a large-scale project. Land acquisition issues further complicated matters, as securing the necessary real estate for the bridge’s approach roads and supporting infrastructure proved contentious and time-consuming. Environmental concerns also played a significant role, with rigorous assessments needed to ensure minimal ecological disruption. Legal battles and public opposition added to the delays, alongside the technical challenges of constructing a bridge in a marine environment prone to harsh weather conditions. These factors collectively caused several false starts and prolonged the timeline, pushing the project back by decades. However, persistent efforts, evolving technology, and increased political will eventually set the project back on track.
Project Significance
Economic Impact
The Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL) is poised to significantly boost Mumbai’s economy. By drastically reducing travel time between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, the bridge will facilitate smoother movement of goods and people, thus enhancing trade and business activities. The improved connectivity is expected to attract investments and promote economic activities in the region, leading to job creation and increased economic output. Additionally, the MTHL will spur real estate development in Navi Mumbai, raising property values and further stimulating economic growth. Overall, the bridge is anticipated to be a key driver of regional economic development.
Connectivity Improvements
The MTHL will transform connectivity between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, cutting travel time to just 20 minutes. This direct route will alleviate congestion on existing roadways and public transport systems, making daily commutes faster and more efficient. Enhanced connectivity will also promote better access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, improving the quality of life for residents. Furthermore, the bridge will integrate seamlessly with existing transportation networks, including highways and railways, providing a comprehensive solution to Mumbai’s traffic woes and supporting the city’s expansion and modernization efforts.
Environmental Considerations
The MTHL project incorporates significant environmental considerations to minimize its ecological impact. Extensive environmental assessments were conducted to understand potential disruptions, leading to the implementation of eco-friendly construction practices. Measures such as careful waste management, use of sustainable materials, and protection of marine life are integral to the project. Additionally, reforestation efforts and the creation of green spaces are part of the mitigation strategies. These efforts ensure that while the bridge enhances urban connectivity, it does so in a manner that respects and preserves the surrounding natural environment, balancing development with sustainability.
Design and Architecture

Structural Design
The MTHL’s structural design is a blend of a sea bridge and an elevated viaduct, extending approximately 22 kilometers, making it the longest sea bridge in India. It features multiple lanes to accommodate heavy vehicular traffic, ensuring efficient flow even during peak hours. The bridge is engineered to withstand harsh marine conditions, with robust foundations and supports designed to endure strong currents and varying soil conditions. Its aerodynamic design helps in mitigating the effects of high wind speeds and seismic activities, ensuring both durability and safety.
Key Architectural Features
The MTHL boasts sleek, modern architectural features that complement its functional design. The bridge includes aesthetic elements such as streamlined shapes and smooth curves that blend seamlessly with the coastal landscape. Illuminated by strategically placed lighting, the bridge creates a striking visual appeal at night. Additionally, the inclusion of pedestrian walkways and observation decks provides scenic views, enhancing the bridge’s appeal. These features not only serve practical purposes but also contribute to the overall aesthetic and cultural value of the structure.
Innovations in Design
Innovations in the MTHL’s design include the use of advanced materials like high-performance concrete and corrosion-resistant steel, ensuring longevity and resilience. The bridge incorporates modular construction techniques, allowing for efficient assembly and maintenance. Aerodynamic design elements reduce wind resistance and improve structural stability. Smart technologies, such as real-time structural health monitoring systems, enhance safety and maintenance efficiency. These innovations reflect a forward-thinking approach, combining cutting-edge technology with practical engineering to create a bridge that is both functional and futuristic.
Construction Timeline
Initial Stages
The initial stages of the MTHL project involved extensive planning and groundwork. This phase included detailed feasibility studies, environmental impact assessments, and comprehensive surveys of the Mumbai Harbour area. Early efforts also focused on securing funding, obtaining necessary clearances, and resolving land acquisition issues. Setting up the logistical framework was crucial, involving the mobilization of resources and machinery. These foundational steps were essential to ensure that subsequent construction phases proceeded smoothly and efficiently, laying the groundwork for the massive infrastructure project.
Major Milestones
Major milestones in the MTHL’s construction include the completion of foundational work and the erection of primary structural components. Key achievements also encompass the installation of main bridge spans and the construction of approach roads. Successful mitigation of initial geological and environmental challenges marked significant progress. The completion of critical supports and roadbeds, along with the integration of advanced safety and monitoring systems, further highlighted pivotal points in the project timeline. These milestones collectively represent substantial advancements towards the bridge’s overall completion.
Current Status
Currently, the MTHL project is in its advanced stages, with most major structural elements completed. Ongoing work includes final road surfacing, installation of safety features, and aesthetic enhancements. The bridge’s smart technologies and monitoring systems are being tested and integrated. With the bulk of heavy construction finished, efforts are now focused on ensuring the bridge meets all safety and operational standards. The project is on track for completion, with final touches being added to make the bridge fully functional and ready for public use.
Construction Techniques and Materials

Advanced Construction Techniques
The MTHL employs advanced construction techniques to ensure precision and efficiency. This includes the use of precast segments, which are manufactured off-site and assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time. Modular construction methods allow for the simultaneous development of different bridge sections. Sophisticated machinery, such as heavy-duty cranes and automated assembly systems, facilitates the precise placement of structural components. Additionally, the project utilizes cutting-edge software for design and structural analysis, ensuring robust construction that meets the highest engineering standards.
Materials Used
The MTHL project uses high-performance materials to ensure durability and resilience. Specially formulated concrete, designed to withstand marine conditions, forms the primary structural material. Corrosion-resistant steel is used extensively to combat the effects of saltwater exposure. Advanced polymers and protective coatings further enhance the durability of key components. These materials are chosen not only for their strength and longevity but also for their ability to reduce maintenance needs, ensuring the bridge remains safe and functional for decades.
Challenges Faced and Solutions
The MTHL project faced significant challenges, including harsh marine conditions, strong currents, and saltwater corrosion. Geological issues, such as varying soil conditions and seabed instability, required innovative engineering solutions. To address these, advanced anti-corrosion coatings and reinforced concrete structures were employed. Specialized construction techniques, such as deep-sea piling and modular assembly, helped mitigate environmental impacts and construction risks. Rigorous safety protocols and continuous environmental monitoring ensured the project progressed smoothly, overcoming these challenges with effective, science-driven strategies.
Engineering Challenges
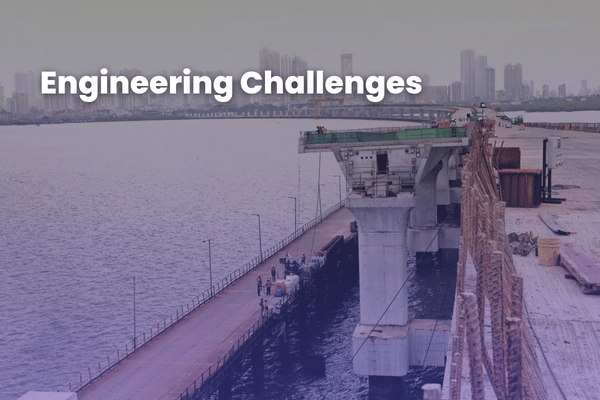
Geological Challenges
The MTHL project faced significant geological challenges, including unstable seabed conditions and varying soil types. Detailed geological surveys revealed shifting sands and weak soil strata, complicating foundation work. To ensure stability, deep-sea piling techniques were employed, driving piles deep into the seabed to anchor the structure securely. Advanced geotechnical engineering solutions, such as ground improvement methods and reinforced foundations, were implemented to address these issues. These strategies ensured that the bridge could withstand geological inconsistencies and provide a stable and durable structure.
Weather and Environmental Conditions
Mumbai’s coastal weather posed considerable challenges for the MTHL project. The region experiences heavy monsoons, high humidity, and strong winds, all of which can disrupt construction activities. Additionally, saltwater exposure increases the risk of corrosion to structural materials. To mitigate these weather-related challenges, construction schedules were carefully planned to avoid monsoon seasons, and materials resistant to corrosion and weathering were used. Protective measures, such as temporary shelters and barriers, were also employed to safeguard ongoing work from environmental impacts.
Mitigation Strategies
To address the various challenges, the MTHL project employed comprehensive mitigation strategies. Anti-corrosion treatments and high-durability materials were used to combat saltwater effects. Advanced construction techniques, such as modular assembly and precasting, minimized environmental disruption. Construction schedules were adjusted to avoid adverse weather conditions, particularly during the monsoon season. Continuous environmental monitoring ensured compliance with ecological standards, while safety protocols protected workers and minimized risks. These strategies collectively ensured that the project progressed smoothly, balancing development needs with environmental and safety considerations.
Safety Measures

Safety Protocols During Construction
During the construction of the MTHL, rigorous safety protocols were implemented to protect workers and ensure project integrity. Regular safety drills and mandatory use of personal protective equipment (PPE) were enforced on-site. Comprehensive training programs equipped workers with knowledge about potential hazards and emergency procedures. Continuous safety audits and inspections identified and mitigated risks promptly. Additionally, advanced monitoring systems tracked real-time safety conditions, ensuring immediate response to any incidents. These stringent safety measures ensured a safe working environment and minimized accidents throughout the construction process.
Safety Features of the Bridge
The MTHL incorporates numerous safety features to ensure user protection and operational integrity. The bridge includes emergency lanes for quick access by rescue vehicles, robust barriers to prevent accidents, and state-of-the-art surveillance systems for continuous monitoring. Additionally, the structure is equipped with advanced lighting for visibility, anti-skid road surfaces to prevent vehicle slippage, and automated traffic management systems to regulate flow and enhance safety. These features collectively ensure a secure and reliable passage for all bridge users, addressing both routine and emergency scenarios.
Technological Innovations

Use of Technology in Planning and Construction
The MTHL project leveraged advanced technology throughout its planning and construction phases. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software facilitated precise structural designs and simulations. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) helped in detailed site analysis and planning. Drones and 3D laser scanning were used for accurate topographical surveys. During construction, Building Information Modeling (BIM) enabled efficient project management and real-time collaboration among stakeholders. Advanced machinery, such as automated piling rigs and heavy-duty cranes, ensured precise and efficient assembly of bridge components. These technological innovations streamlined the construction process, enhancing accuracy, safety, and efficiency.
Smart Bridge Features
The MTHL will be equipped with smart bridge features to enhance functionality and safety. Real-time traffic monitoring systems will provide live updates on traffic flow and congestion, facilitating efficient management. Automated toll collection systems will ensure seamless transactions and reduce delays. Structural health monitoring systems will continuously assess the bridge’s condition, detecting any signs of stress or damage early. Additionally, integrated weather monitoring systems will provide crucial data for maintenance and safety operations. These smart technologies will ensure the MTHL operates smoothly, safely, and efficiently, adapting to both daily use and long-term maintenance needs.
Environmental Impact

Environmental Assessments
Comprehensive environmental assessments were conducted to understand the potential impacts of the MTHL. These studies informed various mitigation strategies to minimize ecological disruption.
Mitigation of Ecological Impact
Efforts to mitigate ecological impact include the use of eco-friendly construction practices, careful waste management, and initiatives to protect marine life. The project also involves reforestation efforts and the creation of green spaces.
Funding and Budget

Financial Planning
The financial planning for the MTHL project involved meticulous cost estimation and resource allocation. Detailed financial models were developed to project expenses across various phases, including design, construction, and maintenance. Contingency plans were established to address potential cost overruns and unforeseen expenses. Regular financial audits and reviews ensured that the project stayed within budgetary constraints. Effective financial planning ensured that the project remained viable and that resources were used efficiently, supporting timely completion and long-term sustainability.
Funding Sources
The MTHL project is financed through a mix of public and private sources. Government grants and loans from national financial institutions provide substantial funding. Additionally, international funding agencies and private sector investments contribute to the financial pool. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) play a significant role, leveraging private investment for public infrastructure development. This diverse funding strategy ensures a robust financial foundation, spreading risk and ensuring adequate capital is available throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Budget Management
Effective budget management is crucial for the MTHL’s success. Continuous monitoring and control mechanisms are in place to track expenditures and manage costs. Regular financial reporting and audits help identify and rectify discrepancies promptly. Cost control measures, such as competitive bidding and value engineering, optimize spending. Allocating funds strategically across various project components ensures that critical areas receive adequate resources. This disciplined approach to budget management ensures the project remains on track, financially sound, and capable of meeting its completion targets.
Stakeholders and Partnerships
Key Stakeholders
The key stakeholders in the MTHL project include the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA), which oversees the project, and various government agencies involved in infrastructure development. Financial institutions, both national and international, provide funding. Construction companies, engineering firms, and technology providers contribute their expertise and resources. Local communities and environmental groups also play a role, ensuring the project meets social and ecological standards. These stakeholders collectively ensure the project’s successful planning, execution, and operation.
Collaborations and Partnerships
The MTHL project involves numerous collaborations and partnerships to harness diverse expertise and resources. The MMRDA collaborates with leading engineering and construction firms for technical and logistical support. Financial partnerships with banks and international funding agencies secure the necessary capital. Technology providers contribute advanced systems for construction and smart bridge features. Environmental agencies and local communities are engaged to ensure sustainable practices. These collaborations and partnerships are crucial for addressing the project’s complex requirements and achieving successful completion.
Future Prospects

Long-Term Benefits
The MTHL promises substantial long-term benefits, including drastically improved connectivity between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, leading to reduced traffic congestion and enhanced economic activities. The bridge will stimulate regional development, attract investments, and create job opportunities. It will also provide a reliable, efficient route for commuters, enhancing their quality of life. Environmentally, the MTHL incorporates sustainable practices, setting a precedent for future infrastructure projects. Overall, the bridge will serve as a catalyst for continued urban and economic growth in the region.
Future Expansions and Upgrades
Future expansions and upgrades for the MTHL are planned to accommodate increasing traffic and technological advancements. Potential developments include additional lanes to manage growing vehicular volumes and integration with upcoming transportation networks like metro lines. Technological upgrades might involve enhanced smart systems for traffic management and structural health monitoring. Regular maintenance and updates will ensure the bridge’s longevity and efficiency. These expansions and upgrades will help the MTHL adapt to future demands, maintaining its role as a critical infrastructure asset.
Public Reception

Public Opinion and Feedback
Public opinion on the MTHL has been largely positive, reflecting widespread anticipation of its benefits. Residents and businesses alike express support for the project, highlighting the expected reduction in travel time and the alleviation of traffic congestion. Feedback from environmental groups has prompted the incorporation of sustainable practices, ensuring ecological considerations are addressed. Regular public consultations and updates have helped build trust and maintain transparency. This positive public sentiment underscores the community’s recognition of the MTHL’s potential to transform regional connectivity and economic prospects.
Impact on Daily Commuters
The MTHL will significantly impact daily commuters by dramatically reducing travel time between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai to approximately 20 minutes. This direct link will ease congestion on existing routes, making commutes faster and more predictable. Enhanced connectivity will improve access to job opportunities, healthcare, and education, enhancing overall quality of life. The bridge’s reliable and efficient route will reduce commuter stress and increase productivity. For many, the MTHL will transform daily travel, providing a smoother, more efficient, and less time-consuming journey.
FAQs
What is the expected completion date of the MTHL?
The MTHL is expected to be completed by the end of 2024, barring any unforeseen delays.
How will the MTHL affect traffic congestion in Mumbai?
The MTHL will significantly reduce traffic congestion by providing a direct link between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, cutting travel time and easing pressure on existing routes.
What are the unique features of the MTHL?
The MTHL features advanced construction techniques, smart bridge technologies, and robust safety measures, making it a state-of-the-art infrastructure project.
How is the project funded?
The project is funded through a combination of government grants, loans from financial institutions, and private investments.
What measures are being taken to protect the environment during construction?
Environmental protection measures include eco-friendly construction practices, careful waste management, and initiatives to protect marine life and promote reforestation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link, or Atal Setu, is more than just a bridge; it’s a testament to modern engineering and a beacon of progress for Mumbai. From its innovative design to the advanced construction techniques employed, every aspect of the project reflects careful planning and execution. As the project nears completion, it stands as a symbol of connectivity, economic growth, and sustainable development.

